The million-dollar question facing skilled nursing facilities today isn’t whether to automate clinical assessments: it’s what to automate. Get this balance wrong, and you’ll either overwhelm staff with unnecessary technology or miss critical opportunities to streamline your admissions process.
Smart automation strategy isn’t about replacing clinical judgment; it’s about amplifying it. The most successful nursing facilities are discovering that the secret lies in automating the right tasks while preserving human expertise where it matters most.
The Current State of Clinical Assessment Chaos
Before diving into automation strategy, let’s acknowledge the reality most admissions coordinators face daily. Manual clinical assessments often involve:
- Sifting through pages of unstructured medical records
- Making countless phone calls to verify patient information
- Manually cross-referencing medication lists and diagnoses
- Spending hours determining if a patient meets clinical criteria
- Coordinating with multiple healthcare providers for missing information
This process typically takes 45-90 minutes per referral, creating bottlenecks that cost facilities both time and potential admissions. But here’s the key insight: not every step in this process requires human intervention.

What to Automate: The High-Impact Areas
Patient Data Collection and Standardization
The foundation of effective nursing facility clinical assessment starts with comprehensive data collection. Automate the gathering and organization of:
Medical History Compilation: AI-powered systems can extract and categorize relevant medical history from multiple sources: hospital discharge summaries, physician notes, and previous facility records. Instead of manually combing through dozens of pages, your clinical team receives organized, relevant information in minutes.
Medication Reconciliation: Automated systems can cross-reference current medications with known interactions, dosing guidelines, and facility formularies. This eliminates hours of manual pharmacy consultation while flagging potential issues for clinical review.
Insurance Verification and Benefits: Real-time insurance verification ensures clinical assessments only proceed for financially viable admissions. Automated systems can verify coverage, determine benefit periods, and calculate estimated reimbursement rates before clinical staff invests time in detailed assessments.
Diagnostic Workflow Optimization
Modern automation excels at routing and processing diagnostic information efficiently:
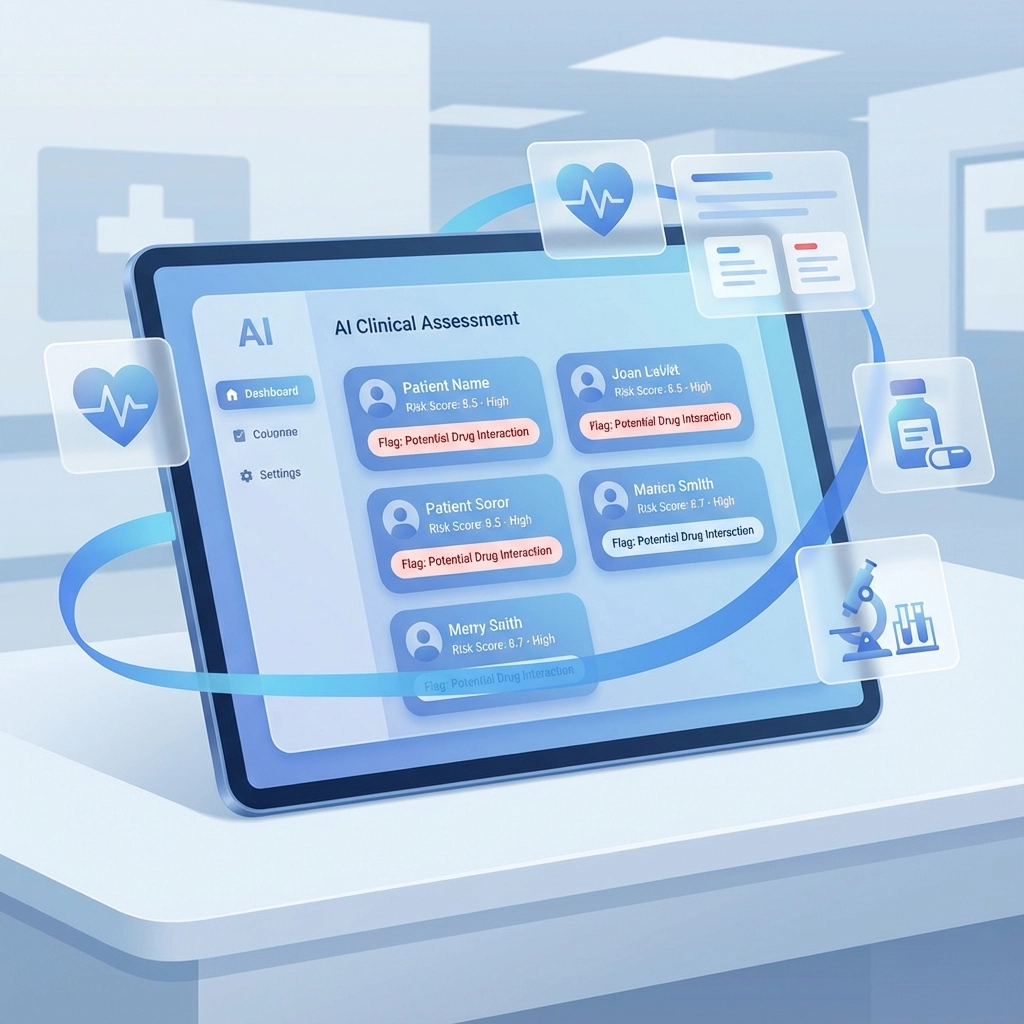
Lab Result Analysis: Automated systems can flag abnormal values, trend critical indicators, and ensure results align with clinical criteria. For example, if a potential admission requires specific hemoglobin levels, the system can immediately identify whether recent lab work meets these requirements.
Risk Stratification: AI algorithms can analyze patient data to assign preliminary risk scores based on fall risk, readmission probability, and care intensity needs. This helps prioritize which referrals receive immediate clinical attention.
Documentation Generation: Automated systems can generate draft assessment summaries and initial care plans based on standardized clinical protocols. These drafts provide starting points for clinical staff rather than requiring them to build assessments from scratch.

Administrative Task Automation
The administrative components of clinical assessment offer significant automation opportunities:
Appointment Scheduling: Automated systems can coordinate assessment appointments with patients, families, and clinical staff while sending confirmations and reminders.
Regulatory Compliance Tracking: Automation ensures all required assessments are completed within mandated timeframes and generates compliance reports for surveyors.
Interdisciplinary Communication: Automated notifications can alert appropriate team members when assessments are completed, when clinical concerns arise, or when additional evaluations are needed.
What to Preserve: The Irreplaceable Human Elements
While automation handles routine tasks brilliantly, certain aspects of nursing facility clinical assessment must remain under human control to maintain quality and safety.
Clinical Judgment and Complex Decision-Making
Nuanced Patient Evaluation: Experienced clinical staff excel at reading between the lines: recognizing when a patient’s presentation suggests underlying issues not captured in documentation. This clinical intuition cannot be automated.
Family Dynamics Assessment: Understanding family dynamics, communication preferences, and decision-making processes requires human empathy and social intelligence that automation cannot replicate.
Ethical Considerations: Decisions involving end-of-life care, advance directives, and complex ethical situations require human judgment and compassion.
Exception Handling and Escalation
Unusual Clinical Presentations: When patients don’t fit standard criteria or present with unique combinations of conditions, experienced clinical staff must make individualized assessments.
Crisis Intervention: Emergency situations requiring immediate clinical intervention need human decision-making and direct patient interaction.
Quality Assurance: While automation can flag potential issues, human oversight ensures the quality and appropriateness of all clinical decisions.

Final Review and Accountability
Clinical Sign-Off: All automated assessments and recommendations require final review and approval by licensed clinical staff. This maintains professional accountability and regulatory compliance.
Care Plan Customization: While automation can suggest initial care approaches, human clinicians must customize plans based on individual patient needs, preferences, and facility capabilities.
Patient and Family Communication: Discussing assessment results, care recommendations, and admission decisions requires human communication skills and emotional intelligence.
Implementation Strategy: The Balanced Approach
Successfully implementing clinical assessment automation requires a thoughtful, phased approach that respects both technology capabilities and clinical expertise.
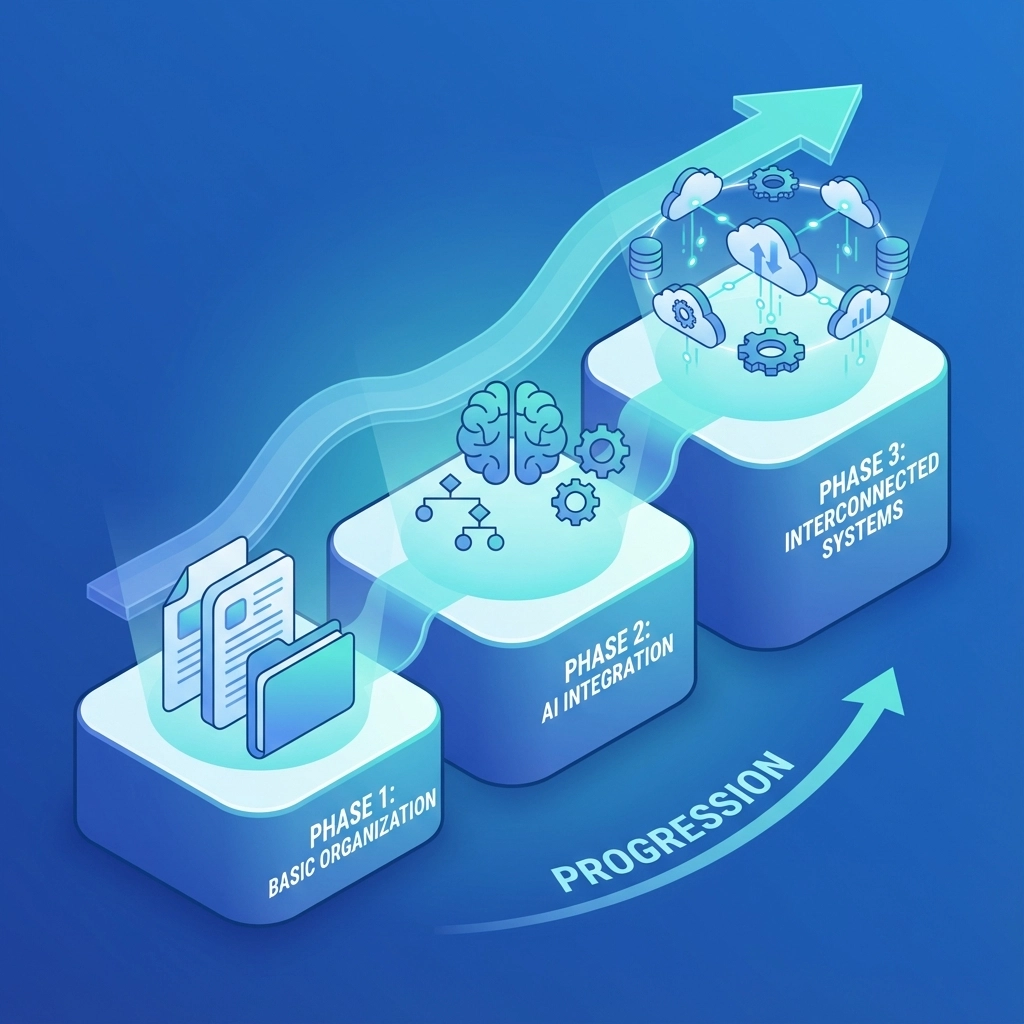
Phase 1: Data Foundation
Begin by automating data collection and organization. Implement systems that:
- Extract and standardize information from referral sources
- Verify insurance and financial information
- Create organized clinical summaries for staff review
This foundation reduces administrative burden while maintaining full clinical control over decision-making.
Phase 2: Decision Support
Introduce AI-powered tools that assist clinical judgment rather than replacing it:
- Risk assessment algorithms that highlight areas needing attention
- Clinical criteria matching that identifies potential admission barriers
- Automated alerts for time-sensitive clinical issues
Phase 3: Workflow Integration
Connect automated processes with existing clinical workflows:
- Integrate with electronic health records
- Automate routine communications and scheduling
- Generate compliance reports and quality metrics
Measuring Success: Key Performance Indicators
Effective automation strategy requires continuous monitoring and adjustment. Track these critical metrics:
Efficiency Gains: Measure reduction in time spent on routine tasks and overall assessment completion times. Successful implementations typically see 50-70% reduction in administrative time.
Quality Maintenance: Monitor clinical outcomes, regulatory compliance scores, and patient satisfaction to ensure automation enhances rather than compromises care quality.
Staff Satisfaction: Survey clinical staff regularly to ensure automation reduces frustration rather than creating new technology burdens.
Financial Impact: Track admission rates, length of stay optimization, and overall revenue per referral to quantify return on automation investment.
The Competitive Advantage
Facilities that master the balance between automation and human expertise gain significant competitive advantages. They respond to referrals faster, make more accurate clinical decisions, and free staff to focus on high-value patient care activities.
More importantly, they create sustainable workflows that can scale with growing referral volumes without proportionally increasing staff workload.
The future of nursing facility clinical assessment isn’t about choosing between technology and human expertise: it’s about strategically combining both to deliver better outcomes for patients, families, and care teams.
Smart automation amplifies clinical judgment rather than replacing it. By automating routine tasks and preserving human oversight for complex decisions, skilled nursing facilities can achieve the efficiency they need while maintaining the clinical excellence their patients deserve.
Ready to optimize your clinical assessment process? Our automation experts can help you identify the perfect balance between efficiency and clinical excellence for your facility. Book a consultation today to discover how the right automation strategy can transform your admissions process.